Introduction
Raising funds is a critical activity for any business, whether it’s a startup seeking capital, a growing company financing expansion, or an established firm managing cash flow. Understanding the various funding sources and their accounting implications is essential for accountants, finance managers, and investors.
This article explores the key methods of funding, including equity, debt, hybrid instruments, and alternative financing, and explains how each is recorded in the financial statements.
1. Ordinary Shares (Common Stock)
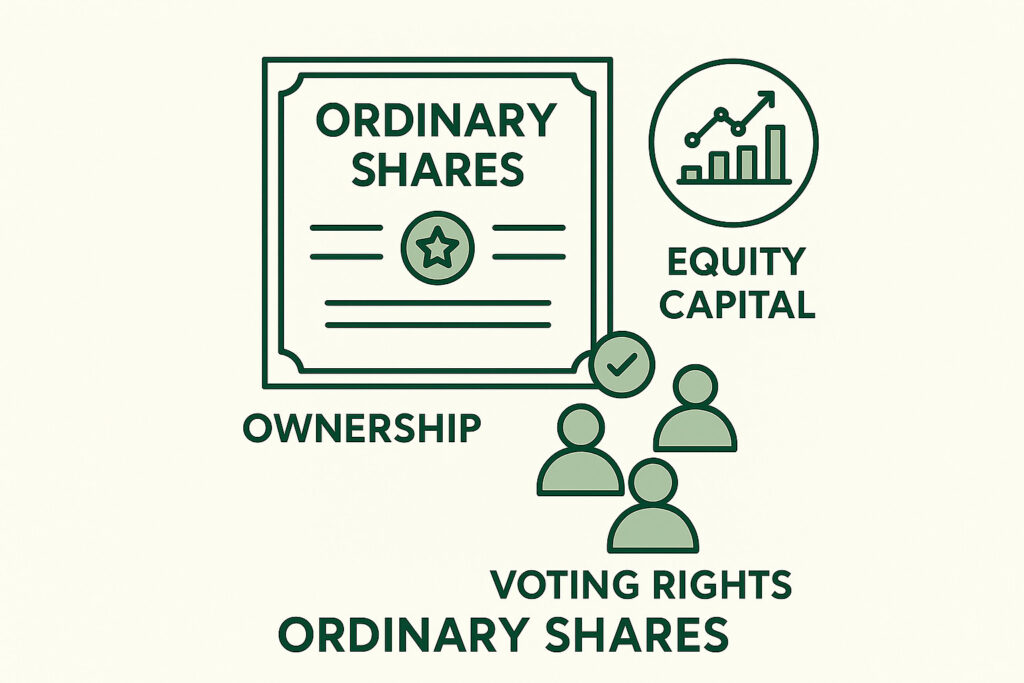
What Are Ordinary Shares?
Ordinary shares represent ownership in a company. Shareholders have voting rights and are entitled to dividends if declared.
Accounting Treatment
When shares are issued:
Example: Issue 1,000 shares at $10 each.
- Entry:
Dr Cash 10,000 Cr Share Capital 10,000
Dividends declared:
Dr Retained Earnings X
Cr Dividends Payable X
2. Preference Shares
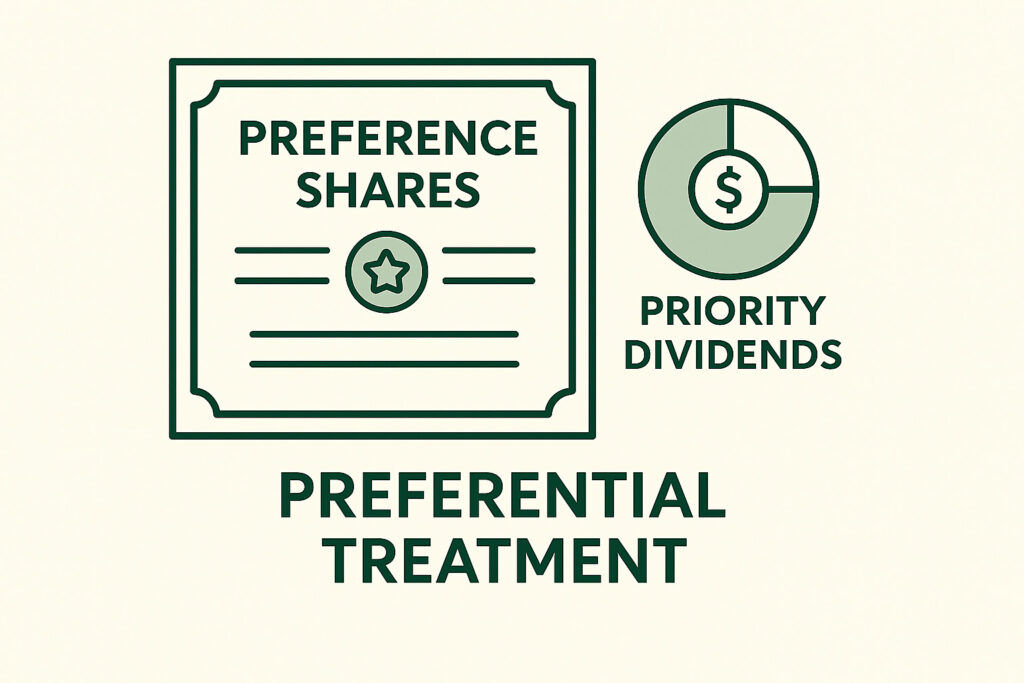
What Are Preference Shares?
Preference shares give holders preferential treatment in dividends and capital repayment but usually do not have voting rights.
Accounting Treatment
Issuing preference shares:
Dr Cash X
Cr Preference Share Capital X
Dividends (cumulative or non-cumulative):
Dr Retained Earnings X
Cr Dividends Payable X
Note: Redeemable preference shares may also require adjustments for premium on redemption.
3. Share Options and Warrants
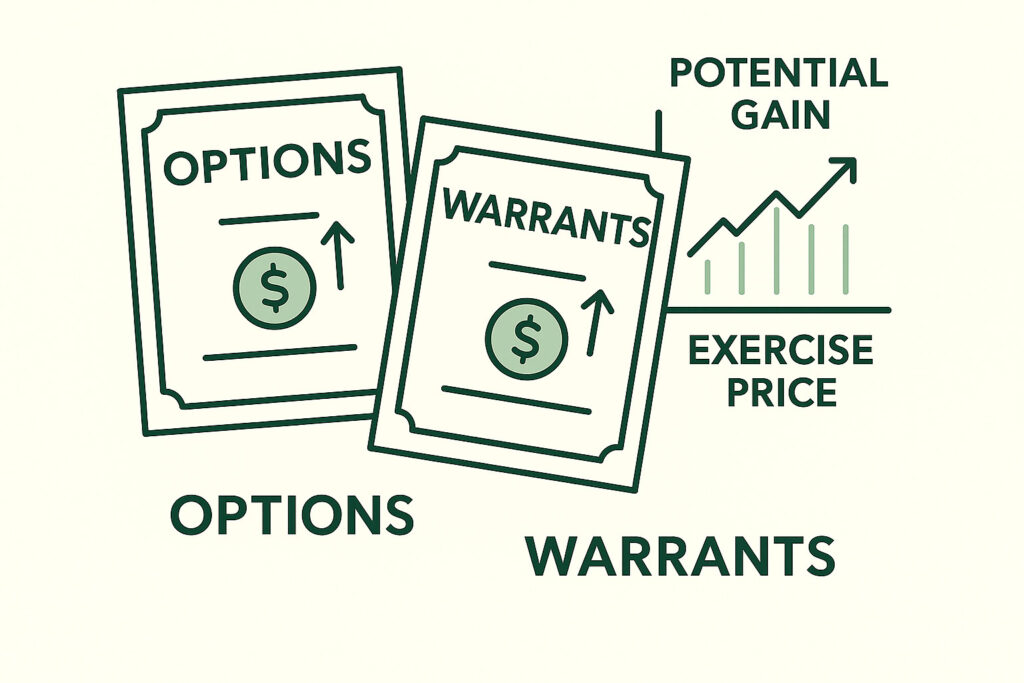
What Are They?
- Options: Right to buy shares at a predetermined price.
- Warrants: Long-term option issued often with bonds or debentures to make them more attractive.
Accounting Treatment
- Recognize proceeds from exercise:
Dr Cash X Cr Share Capital Y Cr Share Premium (X-Y) - If expired without exercise, recognize as income or adjust equity as per company policy.
4. Debentures
What Are Debentures?
Debentures are long-term debt instruments with a fixed interest rate. They are not secured by assets in the case of unsecured debentures.
Accounting Treatment
Issuance of debentures:
Dr Cash X
Cr Debentures Payable X
Interest payment:
Dr Interest Expense X
Cr Cash X
Amortization of premium/discount may also apply if issued at a price different from face value.
5. Bonds
What Are Bonds?
Bonds are long-term debt instruments, usually tradable, issued to raise capital from the public or institutional investors.
Accounting Treatment
- Issuance at par:
Dr Cash X
Cr Bonds Payable X
- Issuance at discount/premium:
Dr Cash X
Dr Discount on Bonds (if below par)
Cr Bonds Payable Y
Interest accrual:
Dr Interest Expense X
Cr Cash/Interest Payable X
6. Convertible Instruments
What Are Convertibles?
Convertibles are bonds or debentures that can be converted into equity at a predetermined rate.
Accounting Treatment
- On issuance: Split into liability (debt) and equity component:
Dr Cash X
Cr Convertible Liability Y
Cr Equity Component Z
- Interest on liability part is recorded normally:
Dr Interest Expense Y
Cr Cash Y
- On conversion:
Dr Convertible Liability Y
Cr Share Capital Z
Cr Share Premium (if applicable)
7. Leasing
What Is Leasing?
Leasing is a method of obtaining assets without full upfront payment. Types include finance lease (capitalized) and operating lease (expense as incurred).
Accounting Treatment
- Finance Lease:
Dr Leased Asset X
Cr Lease Liability X
- Lease payment:
Dr Interest Expense X
Dr Lease Liability Y
Cr Cash (X+Y)
- Operating Lease:
Dr Lease Expense X
Cr Cash X
8. Bank Loans
What Are Bank Loans?
Loans are borrowed funds repayable with interest over a fixed period.
Accounting Treatment
- Loan received:
Dr Cash X
Cr Loan Payable X
- Interest expense:
Dr Interest Expense X
Cr Cash X
9. Factoring
What Is Factoring?
Factoring is selling accounts receivable to a third party (factor) at a discount to improve cash flow.
Accounting Treatment
- On sale of receivables:
Dr Cash X
Dr Loss on Sale of Receivables Y
Cr Accounts Receivable (X+Y)
10. Overdraft
What Is an Overdraft?
An overdraft allows a company to withdraw more than its current account balance, usually up to an agreed limit.
Accounting Treatment
- Recording overdraft:
Dr Cash/Bank X
Cr Bank Overdraft X
- Interest expense:
Dr Interest Expense X
Cr Bank Overdraft/Cash X
Conclusion
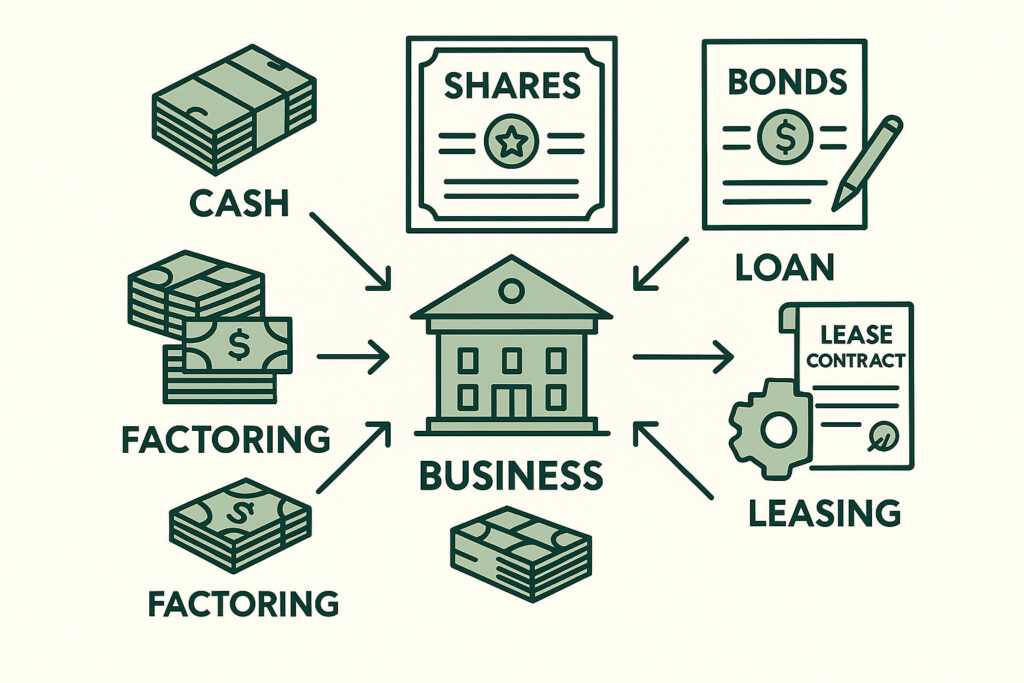
Funding is a cornerstone of business strategy, and understanding different types of funding is vital for proper financial management. Each source—equity, debt, hybrid instruments, and alternative financing—has unique implications on financial statements, control, and cost of capital.
Proper accounting treatment ensures transparency, compliance, and accurate reporting, helping businesses make informed strategic decisions while maintaining investor confidence.